What is an enterprise SEO audit?
An enterprise SEO audit typically refers to exceptionally large websites. If you’ve got 1,000+ URLs, an enterprise SEO audit is precisely what you need.
The first goal of this kind of audit is to evaluate your website to uncover issues preventing you from achieving the most optimal organic search performance. This is accomplished via:
- Technical SEO – Is Google able to crawl all URLs that should be included in their index? Does the site perform well from a UX standpoint?
- Content – Are pages optimized for your targeting keywords? Are those pages meeting searcher intent? Are there additional content opportunities?
The second goal is to identify new performance improvement opportunities available either through optimizing content on existing URLs, or creating new URLs that close data-verified content gaps.
Why is it important to do an enterprise SEO audit?
An enterprise SEO audit is an essential part of any SEO strategy for large websites. It can help you identify and fix any issues that are preventing your website from ranking well in search engines.
Here are some of the benefits of conducting an enterprise SEO audit:
- Identify and fix technical SEO issues. A technical SEO audit can help you identify and fix any technical issues that are preventing your website from being crawled and indexed by search engines. This includes issues such as broken links, duplicate content, and poor page loading speed.
- Optimize your content for search. An enterprise SEO audit can help you optimize your content for search by identifying the right keywords and phrases to target. It can also help you improve the overall quality of your content, making it more likely to rank well in search results.
- Improve your website’s user experience. An enterprise SEO audit can help you improve your website’s user experience by identifying any usability issues that may be preventing users from finding the information they need. This can lead to an increase in organic traffic and conversions.
- Track your progress and measure your results. An enterprise SEO audit can help you track your progress and measure the results of your SEO efforts. This information can be used to fine-tune your SEO strategy and ensure that you are getting the most out of your investment.
If you have a large website, an enterprise SEO audit is a valuable tool that can help you improve your website’s visibility in search engines. By identifying and fixing any issues that are preventing your website from ranking well, you can increase your organic traffic and improve your website’s overall performance.
How To Do An Enterprise SEO Audit
You already understand the basic premise of SEO (search engine optimization):
Employ a range of strategies – everything from granular content optimizations to data architecture enhancements – to improve how your site ranks for your relevant search terms.
But SEO optimizations for a gardening blog versus an enterprise website will look a bit different, so today, we’re laying out a clear game plan for conducting an enterprise SEO audit.
Enterprise SEO Audit Checklist
You can’t put a price on the satisfaction that comes from a well-placed checkmark or a bold line crossing off an item from a long to-do list. But before we get to the SEO audit checklist, a word of caution…
While a checklist certainly helps to ensure that you cover the basics during your audit process, conducting a successful SEO audit takes curiosity and investigation. This is doubly true when the site in question belongs to an enterprise brand with a complex information architecture.
The willingness to thoroughly investigate the full SEO picture (coupled with the skills to pull that off) puts you in the best position to uncover hidden issues and opportunities that will otherwise fly under the radar of even the most thorough of SEO checklists.
Next, you need a spirit of curiosity to determine the root cause of those issues (there are often overlapping factors that need to be examined closely). This kind of ‘SEO sleuthing’ work requires a meticulous eye, but often leads not just to the resolution of something that’s working against your SEO performance, but also to optimization opportunities hiding in plain sight.
The point we’re trying to make here is:
SEO audits are not a quarterly activity to be rushed off the project calendar. They need to be conducted by a team with proven subject matter expertise, attention to detail, and a high degree of “Determined Detective” vibes.
Okay, so now that you’ve heard our caution, let’s get into the exact steps you need to take.
While conducting Google searches and manually looking through the website’s content will be necessary, there are a number of tools to make an SEO audit less time consuming and successful, so we’ve included links to a few of our favorites in the checklist below.
Get a free copy of our Enterprise SEO Audit Checklist:
Step 1: Process definition
- Define the website’s purpose, audience, and goals.
Before you roll your eyes in “Duhhh, that’s obvious” disappointment, hear us out.
Many high profile brands are relying on heavy ad budgets largely because their organic search performance is mediocre at best, abysmal at worst. And yet, most of these brands have mechanisms in place to conduct regular SEO audits either through in-house resources or an SEO agency, which makes them think that they’re already doing all the right things so they have no choice but to accept their lackluster Google results.
But we haven’t yet seen a single case where that was actually true.
You cannot conduct an effective enterprise SEO audit without well-defined goals, and clarity on the exact (exact!) audience those goals apply to.
All that investigation and curiosity we mentioned earlier? It’ll amount to a tiny flashlight in a dark room if these foundational details aren’t ironed out first because you won’t be clear on the results you’re seeking, and the ones you want to optimize for.
Your target keywords, content strategy, and meta descriptions will either be wildly mismatched (reducing acquisition and therefore, conversion volume), or you’ll only see conversions from an audience that doesn’t mirror the strategically-selected audience profile that your paid media and other acquisition tactics are targeting.
Get clear on why you’re doing this audit in the first place, and then move onto:
- Create a project roadmap that defines each phase of the process, and make sure to include performance benchmarks and a detailed timeline.
- Confirm full process buy-in from both your technical and content teams
Step 2: Technical audit
So, here’s our technical checklist recommendations for enterprise brands:
- Crawl your website. Use a tool like Screaming Frog to crawl your entire site. Crawl data can be used for taking stock of all website URLs, checking response codes, understanding URL structure, seeing metadata, checking inbound links, and more.
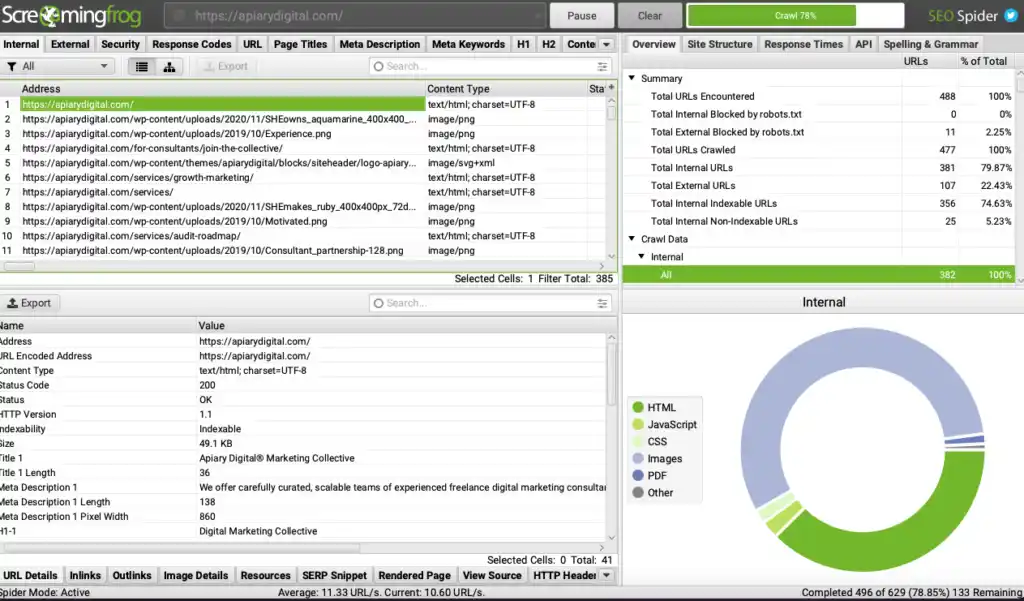
In addition to collecting and viewing website data, Screaming Frog can also run reports that make the technical health of your site more visible, including redirect issues, broken links, and hreflang errors.
- Inspect Google Search Console to see how Google views and crawls your website.
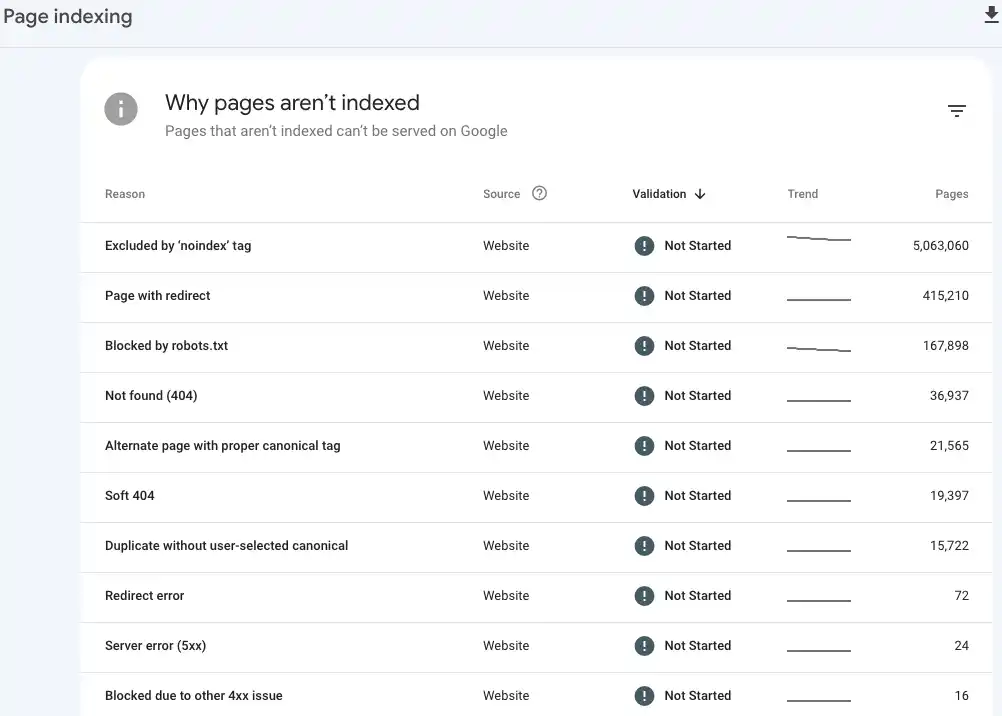
- Look at pages being indexed and not indexed. Are there pages being excluded from search results that should be included? Are there pages that have no value that are eating up crawl budget? Are there 404s that should be 301 redirects elsewhere?
- Has a Sitemap been submitted to Google and are there any errors on it?
- Are URLs failing Core Web Vitals? Is the website usable on mobile devices?
- Does Google detect schema markup on the website and are there any errors that need to be fixed?
- Are there manual actions or security issues that need to be addressed?
- Conduct site searches on Google to weed out additional URL types that shouldn’t be indexed. For example, to find URLs that are using parameters, search site:www.mywebsite.com/inurl: “?” or whatever you think the parameter might include.
- Create a single data source. Put your website crawl data, Screaming Frog reports, and Google Search Console data into a spreadsheet that will function as your single source of truth while fixing technical issues.
Step 3: Content audit
Auditing a website’s content ensures the right keywords are being targeted, pages are optimized to rank organically, and the content you’ve invested in creating is actually meeting searcher intent.
- Conduct keyword research and compile a list of keywords to target.
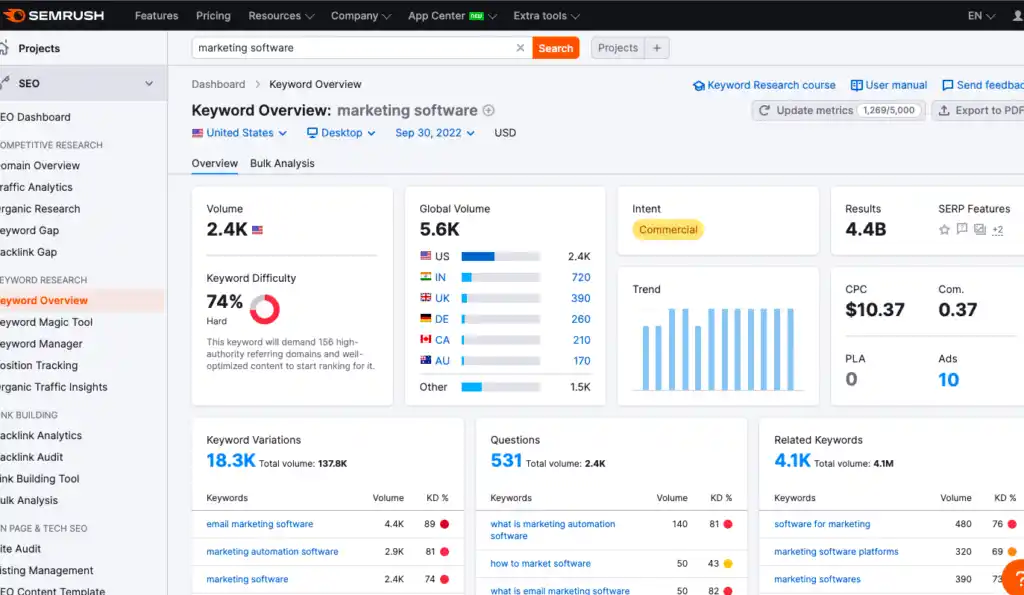
- What keywords or topics are strategically valuable? Identify those head terms/topics and use a tool like SEMRush or Keywords Everywhere to compile lists of long-tail keywords within those keyword buckets.
- Look at competitors, both websites that are thought to be direct competitors and any sites that are ranking well for your keyword topics. Again, use something like SEMRush to see what URLs are performing well for them, and what keywords those pages are targeting.
- Analyze keyword data in Google Search Console (GSC), especially non-branded keywords.
- Use GSC keyword data to uncover cannibalization issues. Are there multiple URLs fighting to rank well for one keyword? Should those pages be combined or better optimized to target different keywords?
- Are there URLs or keywords that are generating a high number of impressions but not seeing many clicks? These would be optimization opportunities.
- Prioritize top level keywords/topics to be targeted by core webpages. Once topics and keywords have been identified and compiled, pages such as category URLs or blog posts should be used to target long tail keywords.
- Map keywords to existing URLs
- Use remaining keywords to drive new content initiatives
- Identify search intent for target keywords. Use SEMRush or conduct Google searches to identify search intent for target keywords. Does informational, transactional, or navigational content perform best? These results should inform your ongoing content strategy for all channels – web, email, organic social media, and paid.
- Check on-page optimization
- Write/rewrite URL metadata to follow best practices and target keywords, including title tag, meta description, and H tags.
- Write/rewrite page content to meet searcher intent
- Include target keyword in URL slug
- Write/rewrite image alt tags to include target keyword
- Use target keywords for anchor text in internal links. Conduct site searches (www.mywebsite.com/“keyword”) to find link opportunities
- Use Copyscape to check for duplicate content
Step 4: Backlink audit
External backlinks have long been a powerful ranking signal. Having a quality backlink profile tells Google that a website is trustworthy and should be viewed as an authority in its niche.
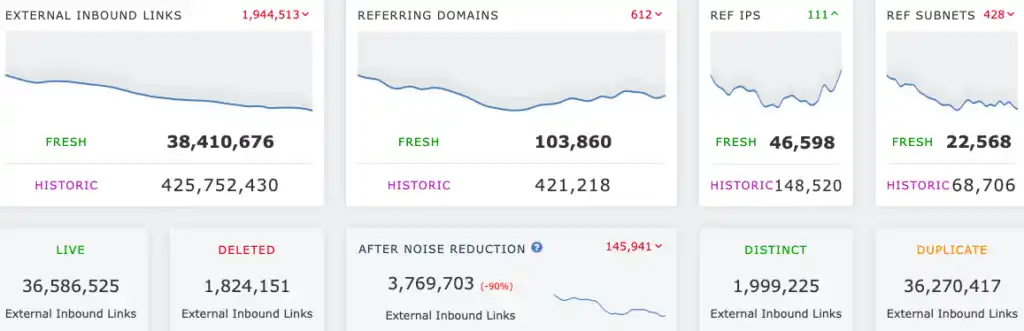
- Use a tool such as Majestic to take stock of existing backlinks. Are there spammy links that you should ask to be removed or disavowed? Are there valuable links going to URLs that are actually 404s and should become 301 redirects instead?
- Again, use Majestic to compare your website’s backlink profile to competitors. Competitor’s backlinks can represent new opportunities.
- Outline your strategy for building new links.
What to Include In Your Enterprise SEO Audit Template
While your enterprise SEO audit is being conducted, keep track of findings and opportunities in a Google Presentation deck. (Yes, we recommend the Google suite, but if you’re still attached to Microsoft, use whatever works for you. We can still be friends.) Compile any necessary data in a Google Spreadsheet.
It’s important that findings are housed in these two locations only to ensure visibility and to provide a central task management overview for the members of your team who’ll be involved.
You can structure these two components of your audit template however you like. Below, we’ve shared the key elements we believe should always be included.
Presentation Deck Slides
- Website Performance & Goals Looking Forward
- Organic traffic (Google Analytics)
- Top performing URLs (Google Analytics)
- Goal Conversions (Google Analytics)
- Top performing keywords (Google Search Console)
- Goals going forward
- Technical Issues
- XML Sitemap
- Robots.txt
- Mixed content
- Redirect chains
- 404 errors
- Orphaned URLs
- Broken links
- Hreflang errors
- Canonical tag issues and recommendations
- Core Web Vitals
- Structured data errors and recommendations
- Site structure/navigation recommendations
- Backlinks
- Content Recommendations
- Keyword topics
- Competitor analysis
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- H tags
- Image optimization
- New content opportunities
- Next Steps
- SEO Roadmap
Spreadsheet Tabs
- Technical Audit
- Website crawl
- 404 errors with necessary redirects
- Redirect chains
- Orphaned URLs
- Broken links
- Hreflang errors
- Canonical errors and recommendations
- Recommended site architecture
- Existing backlinks
- Competitor backlinks
- Content Audit
- Priority keywords
- All keywords (one topic per tab)
- Optimization recommendations
- New content recommendations
Summary: Enterprise SEO Audit
An enterprise SEO audit is ultimately about efficiency and performance.
The goal of the audit is to determine if your website is as healthy as it is beautiful, and more effectively guide your team’s time, resources, and budget.
In the world of digital marketing, optimizations are always the name of the game, and an enterprise SEO audit exists to identify those optimization opportunities so that your brand can rise up the organic search rankings.




